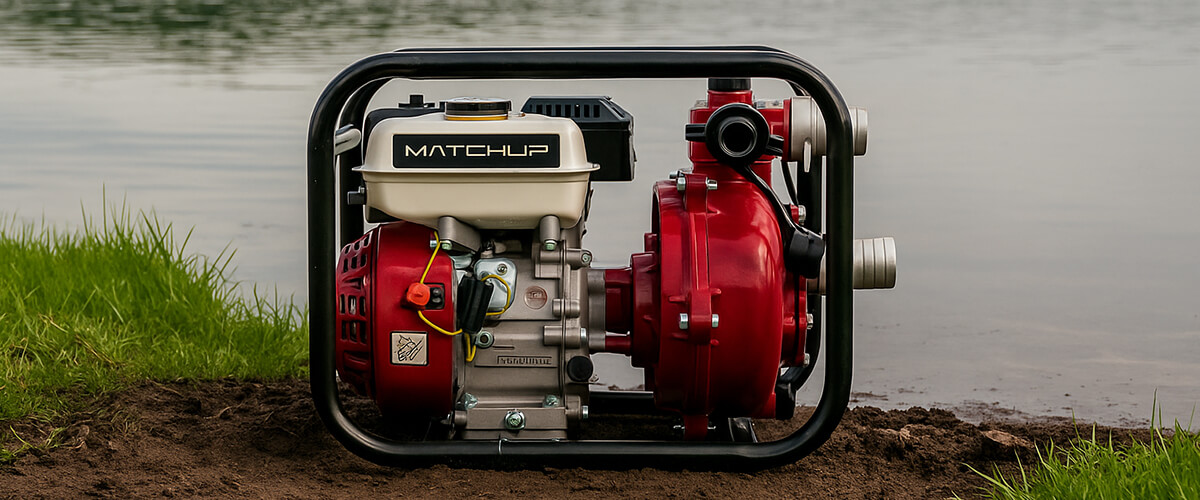
gasoline water pumps
Gasoline pumps are reliable solutions for efficient water transfer in agricultural, construction, and emergency applications. At MATCHUP, we manufacture high-quality, durable, and fuel-efficient gasoline-powered water pumps designed to handle clean water, muddy water, and debris-laden liquids.
OEM/ODM water pump manufacturers
gasoline water pump manufacturers and suppliers
As a leading OEM manufacturer in China, MATCHUP provides wholesale gasoline water pumps that meet international standards. Our pumps are built for high efficiency, easy maintenance, and long-lasting performance, making them a top choice for professionals worldwide.
Whether you need a pump for irrigation, flood control, or industrial use, MATCHUP offers models to meet different flow rates and pressure requirements.
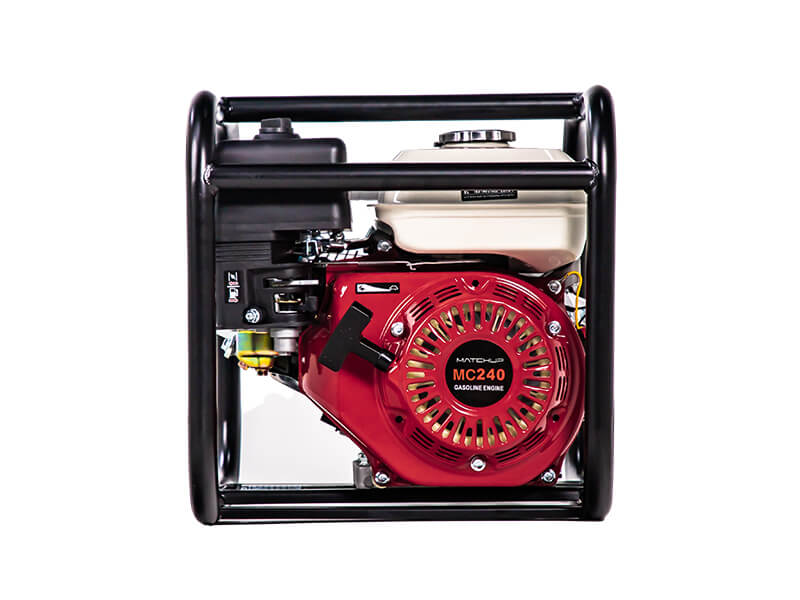
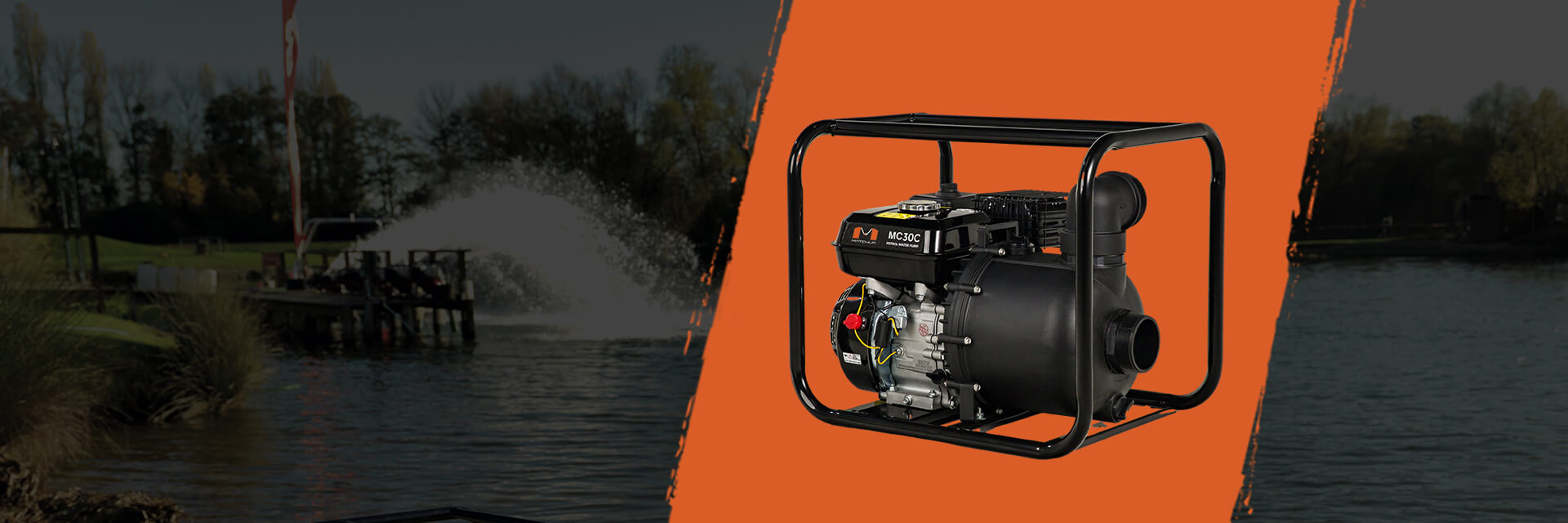


professional water pumps manufacturer
Typical applications of gasoline water pumps
Gasoline water pumps are incredibly versatile and can be used in a wide range of situations. Here’s a breakdown of key areas where they’re most useful:
Agriculture and Irrigation
Gasoline water pumps are widely used for irrigation, distribution, and drainage in farms and gardens. Farmers rely on them to transport water from rivers, lakes, or reservoirs to their fields, ensuring a consistent water supply for crops. These pumps are especially valuable in areas with limited access to electricity. High-pressure models can also be used to spray pesticides and fertilizers over large areas or to drain waterlogged fields after heavy rain, protecting crops from damage.
Construction and site dewatering
On construction sites, water accumulation in trenches, foundations, and excavation zones can cause delays and structural issues. Gasoline water pumps are essential for quickly removing excess water, helping maintain a dry and safe job site. Trash pumps are particularly useful here, as they can handle mud, sand, and debris without clogging, ensuring smooth and continuous operation.
Flood control and emergency water removal
During heavy rains or natural disasters, gasoline water pumps offer a reliable solution when electricity is unavailable. They are used to drain floodwater from homes, basements, streets, and industrial areas. Emergency response teams often depend on these pumps to clear standing water, minimize property damage, and speed up recovery efforts in affected communities.
Firefighting
High-pressure gasoline water pumps are essential in firefighting, especially in remote or rural areas without hydrant access. These pumps can draw water from ponds, lakes, or tanks and deliver a powerful stream to control or extinguish fires. They are also used in fire suppression systems for large buildings and industrial facilities.
Industrial use
In factories and industrial facilities, gasoline water pumps are used for tasks like water transfer during maintenance, cleaning processes, or equipment cooling. They’re particularly helpful for removing water from tanks, pipes, or other systems where temporary or backup pumping is needed, and electric pumps are not feasible.
Residential water transfer and drainage
Gasoline water pumps are practical for many home-based tasks. Homeowners use them to drain swimming pools, clean ponds, remove stormwater, or empty flooded basements. Their portability makes them ideal for areas without convenient access to electricity. They’re also used to transfer water between storage tanks or in off-grid homes relying on rainwater harvesting systems.
Mining and oil exploration
In mining operations, groundwater accumulation in pits and tunnels can halt excavation and pose safety risks. Gasoline water pumps help manage water levels, ensuring smooth and safe operations. They’re also used on oil exploration sites to move water efficiently and maintain site stability during drilling activities.
How to choose the right gasoline water pump
Imagine you’re in a remote village where a sudden flood threatens homes and farmland. The roads are inaccessible, and electricity is down. That’s when a gasoline water pump comes to the rescue. With its powerful engine, it quickly drains the floodwater, saving lives and crops. In another scenario, a farmer without an electrical supply needs to irrigate his fields. A gasoline water pump moves water from nearby sources directly to the crops.
A gasoline water pump is powered by a gasoline engine and designed to move water quickly and efficiently. It’s an essential tool for situations where electricity isn’t available or reliable. These pumps are known for their strong performance, portability, and independence from power grids. They’re useful for everything from emergency flood control to daily irrigation.

Advantages of gasoline water pumps
Gasoline water pumps offer several advantages over electric and diesel models, making them a top choice for a variety of tasks. Here’s why they are the preferred choice for many industries:
- Portability and independence: One of the greatest advantages of gasoline water pumps is their portability. Since they don’t require electricity, you can use them anywhere—whether you’re out in the field, at a construction site, or during a flood emergency. Their self-contained engine allows them to be used in remote locations, agricultural fields, and emergencies where electricity is unavailable, providing flexibility in various applications.
- Strong power: Gasoline water pumps are designed to handle large volumes of water quickly, offering strong performance for big jobs like irrigation, flood control, or transferring water at job sites. With a high flow rate and strong suction and discharge capabilities, they complete tasks efficiently, making them more powerful than electric pumps and ideal for heavy-duty use.
- Durability and reliability: Built with tough materials like cast iron, aluminum, and stainless steel, gasoline water pumps resist wear, corrosion, and harsh conditions. Their rugged construction allows them to operate continuously in demanding environments, ensuring reliability and long-term performance without frequent breakdowns.
- Versatility: Gasoline water pumps come in various types—including clean water, trash, semi-trash, high-pressure, and chemical pumps—making them suitable for home, industrial, agricultural, and emergency applications. Their ability to adapt to different tasks makes them a smart and versatile investment.
Types of gasoline water pumps
Choosing the right gasoline water pump depends on the type of water you need to move. Here are the most common types:
When it comes to gasoline water pumps, there are several types, each designed for specific tasks. Let’s look at the main types of gasoline water pumps, how they work, and what they’re best suited for.
- Clean water pumps: Clean water pumps are designed to move clean or slightly dirty water without large debris. They are commonly used for irrigation, pond drainage, and water supply to homes or businesses. These pumps have fine intake filters to prevent clogging and are ideal for applications where water purity is essential.
- Trash water pumps: Trash water pumps handle muddy water, sand, and debris. With large impellers and robust casings, they prevent clogging and damage. These pumps are used in flood control, construction sites, and sewage management—anywhere the water contains solid particles like dirt, leaves, or small rocks. Trash pumps are built for heavy-duty use in rugged conditions.
- Semi-trash water pumps: Semi-trash pumps offer a middle ground between clean water and trash pumps. They can handle small debris but are not suited for large solids. These pumps are often used in agriculture, minor flooding, and construction water treatment, where slightly dirty water needs to be moved efficiently.
- High-pressure water pumps: High-pressure water pumps generate strong water flow at high PSI (pounds per square inch). They are ideal for firefighting, long-distance irrigation, and agricultural spraying. Unlike pumps designed for high volume, these focus on pushing water over longer distances.
- Chemical and fertilizer pumps:
These pumps are built from noncorroding materials to safely transfer fertilizers, pesticides, and other corrosive liquids. Commonly used in agriculture, chemical processing, and industrial applications, they resist damage that would occur with standard pumps exposed to harsh chemicals. - Transfer water pumps: Transfer pumps are designed for high-speed water movement, not for handling debris or high pressure. They are ideal for emptying tanks, filling reservoirs, and emergency water transfers—perfect when large volumes of clean water need to be moved quickly and efficiently.
How to choose the right gasoline water pump?
Choosing the right gasoline water pump doesn’t have to be overwhelming—just focus on a few key factors that make the most sense for your specific needs. Here’s what to look for:
Determine the type of water you want to pump
The first and most important step is to understand the type of water you need to move.
- Clean water: If the water is clean and free of debris (e.g., pools or reservoirs), a standard centrifugal pump is sufficient.
- Dirty water: If the water contains mud, sand, or debris (e.g., from floods or construction sites), you’ll need a trash pump that can handle solids without clogging.
- High-pressure needs: For applications like firefighting or long-distance irrigation, a high-pressure pump is ideal.
- Chemical or corrosive liquids: Use a chemical pump made with corrosion-resistant materials if you’re handling hazardous or reactive liquids.
Consider the pump’s flow rate and capacity
Flow rate indicates how much water the pump can move per minute, usually measured in GPM (gallons per minute) or LPM (liters per minute).
- Low flow rate (50–150 GPM): Suitable for small-scale applications such as garden watering or household drainage.
- High flow rate (200+ GPM): Ideal for large-scale irrigation, flood control, or construction site dewatering.
Choosing the correct flow rate helps you complete the task efficiently and avoid excessive fuel consumption.
Check the pump’s maximum head and suction lift
- Maximum head: This is the maximum vertical distance the pump can push water. It’s crucial for uphill or long-distance pumping. For example, if you need to move water to an elevated tank or across a large site, choose a pump with a higher head rating (80–150 feet or more).
- Suction lift: This refers to how high the pump can draw water from its source (like a well, stream, or pond). Most gasoline water pumps offer a suction lift capacity of about 20–25 feet. If your water source is located lower than the pump, be sure it can handle that depth effectively.
Engine type (two-stroke vs. four-stroke)
Two-stroke engines are lightweight and simple, making them a good choice for portable pumps used for occasional tasks. However, they tend to consume more fuel and require more maintenance. Four-stroke engines are more fuel-efficient and generally need less maintenance, making them ideal for regular or heavy-duty use. Consider how often you’ll be using the pump and how much maintenance you’re willing to do.
Assess the engine power and fuel efficiency
The engine’s power, measured in horsepower (HP), determines the pump’s strength and capacity. Higher HP means the pump can move more water and handle tougher tasks such as flood cleanup, irrigation, or construction site work. Choose a pump with enough horsepower to meet your specific needs.
Fuel efficiency affects how long the pump can operate on a full tank. A fuel-efficient pump lets you work longer without refueling, reducing downtime. Look for a good balance between power and fuel consumption, and consider features like automatic idle control, which lowers fuel use when the pump is idle.
Noise levels
Noise can be a concern, especially in residential or quiet areas. If working in noise-sensitive environments, select a pump designed for low-noise operation or with noise-reducing features. This helps minimize disturbance to the surrounding environment.
Portability
Portability is essential if you need to move the pump frequently. Consider the size, weight, and whether the pump includes features like handles or wheels for easier transport. Lightweight and compact pumps are ideal for small tasks, while heavier-duty models are necessary for larger jobs but should still be manageable to carry or wheel around.
Check port size and hose compatibility
The inlet and outlet port sizes determine how much water flows through the pump. Standard sizes range from one inch to six inches. Smaller pumps (1–2 inches) are ideal for home and garden use, while larger sizes (3–6 inches) are needed for flood control, construction, and industrial applications. Ensure the pump is compatible with the hoses, fittings, and accessories you plan to use.
Check the pump’s durability and build quality
A gasoline water pump should be made of high-quality materials to withstand harsh conditions. Look for pumps with cast iron or aluminum housings, sturdy impellers, and stainless-steel components for long-lasting durability. If used in rugged environments, choose a model with a protective frame to prevent damage.
Look for solid build quality—durable materials and reliable engineering will ensure your pump lasts longer and performs better. Stick with trusted brands that offer good customer support and warranties, so you’re covered if anything goes wrong. A reputable brand can make a big difference overall.
Budget and long-term costs
While it might be tempting to choose the cheapest pump, balance your budget with long-term costs. Consider factors like fuel efficiency, maintenance needs, and durability. A slightly higher upfront cost may save you money over time if the pump is more efficient and lasts longer.
Evaluate safety features and maintenance requirements
Safety features such as low oil shutoff, thermal protection, and overload protection help prevent engine damage and extend pump life. A pump with easily accessible air filters, spark plugs, and fuel tanks makes maintenance easier. Regular servicing ensures reliable performance and prevents breakdowns during critical operations.
Summary of key points
Gasoline water pumps are powerful, portable, and reliable machines designed to move water efficiently where electricity isn’t available. These pumps use gasoline engines, offering a flexible solution for various tasks—whether it’s draining floodwater, irrigating crops, or cleaning construction sites.
When choosing the right pump, consider factors like lift height (head), flow rate, the type of water you’ll be pumping, suction lift, and engine type. By understanding the task at hand and the features you need, you’ll be able to select a pump that fits your requirements perfectly.
Ready to make a smart investment in your water-moving needs? Explore MATCHUP range of reliable gasoline water pumps—built to deliver exceptional performance, durability, and flexibility. Whether you’re tackling a small residential project or a large-scale industrial task, our pumps meet the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Purchase premium gasoline water pumps from MATCHUP, a trusted OEM in China. Get competitive wholesale prices and expert support. Contact us today!
about gasoline pressure water pumps, people also ask:
How often should I service my petrol water pump?
Maintaining your petrol water pump is easier than you think, and regular maintenance can keep it running smoothly and performing at its best for many years. Here is a simple guide to help you keep your water pump in top shape:
- Change the oil – Regularly changing the oil keeps your engine running smoothly. Check the manufacturer’s instructions for the recommended change interval, which is usually every 50-100 hours of use.
- Clean the fuel system – Dirt and debris can clog the fuel system over time. Clean the tank and fuel lines to prevent buildup. Use fresh fuel and avoid leaving old fuel in the tank.
- Change the filter – Check your air and fuel filters regularly. A clogged air filter can reduce engine performance, while a dirty fuel filter can affect fuel flow. Replacing these filters is an easy and cost-effective way to maintain your water pump.
- Check the spark plugs – Spark plugs are essential for engine starting. Make sure they are clean and in good condition. Replace worn or dirty spark plugs for easier starting.
How do I store my pump during the off-season?
Drain all fuel, clean the pump, and store it in a dry place to prevent rust and damage.
How does a gasoline water pump work?
A gasoline water pump works by using a gasoline engine to move water from one place to another. Whether draining floodwater or irrigating crops, this process ensures reliable water movement in various conditions.
Let’s break it down into simple parts to help you understand how it works. The main parts of the pump include:
- Gasoline engine: The heart of the pump, it runs on gasoline and provides the power needed for operation.
- Pump unit: Contains the components that move the water, including the inlet and outlet.
- Inlet and outlet ports: The inlet draws water in; the outlet pushes it out. Hoses are connected here to direct water flow.
- Fuel system: Supplies gasoline to keep the engine running.
- Starting mechanism: Some pumps use manual start (pull cord), while others use electric start (push-button).
How It works?
- Suction: A gasoline water pump uses an internal combustion engine to drive an impeller inside the housing.
- Discharge: When the engine is running, the impeller rotates, creating suction that draws water into the inlet and pushes it out through the outlet.
- Flow and pressure: The engine’s strength affects how much water is moved (flow) and how forcefully it’s pushed (pressure). A stronger engine increases both.
Common gasoline water pump problems and solutions
Even with regular maintenance, sometimes things don’t go as planned. Here are the steps to take when you encounter common problems:
Water pump fails to start
- Possible causes: The spark plugs may be dirty, the fuel may be old, or the fuel line may be clogged.
- Solution: Check the spark plugs and clean or replace them as needed. Drain the old fuel and replace it with new fuel. Check the fuel line for any blockages.
Water pump loss of pressure
- Possible causes: A clogged filter or a problem with the suction line.
- Solution: Clean or replace the filter and check the suction hose for kinks or leaks. If you are getting water from a water source, make sure the hose is completely submerged in water.
Unusual noises
- Possible causes: Loose engine parts, low oil, or a problem with the water pump housing.
- Solution: Check the oil level and top it up if it’s low. Check the engine and oil pump for any loose bolts or parts and tighten as needed.
Excessive fuel consumption
- Possible causes: A dirty air filter or incorrect engine settings.
- Solution: Replace the air filter and make sure the engine is tuned correctly. If fuel consumption is still high, check the carburetor or consult a professional for a tune-up.




